Fintech in Indonesia
Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Momentum Work View’s on Fintech landscape
- Overview of Indonesia
- Opportunities and risks for Fintech players
- Current economic and technological aspect
- Bank distribution & penetration in Indonesia
- Financial loan needs VS gap
- Payment culture
- Overview of Indonesian Fintech
- Fintech ecosystem and certified players
- Market composition
- Indonesia Fintech Development from 2009-2019
- Regulatory structure & licenses
- Payment Systems
- BI regulation toward payment-related services
- License procurement & e-money transactions
- Payment gateway main players
- Exhibit: Doku payment ecosystem
- E-wallets
- E-wallet landscape
- Developments and suspended operations
- E-wallet main players
- Exhibit: OVO strategic partnership
- P2P Lending
- OJK regulatory environment
- Revoked/suspended P2P registration
- License procurement procedure
- P2P infrastructure & main players
- Investment
- Exhibit: VC funding in Indonesia Fintech
- Risks
- Major risks: Political and regulatory
- Major risks: Operational
- Major risks: Reputational
- Major risks: Currency
- MW Insights
- Glossary
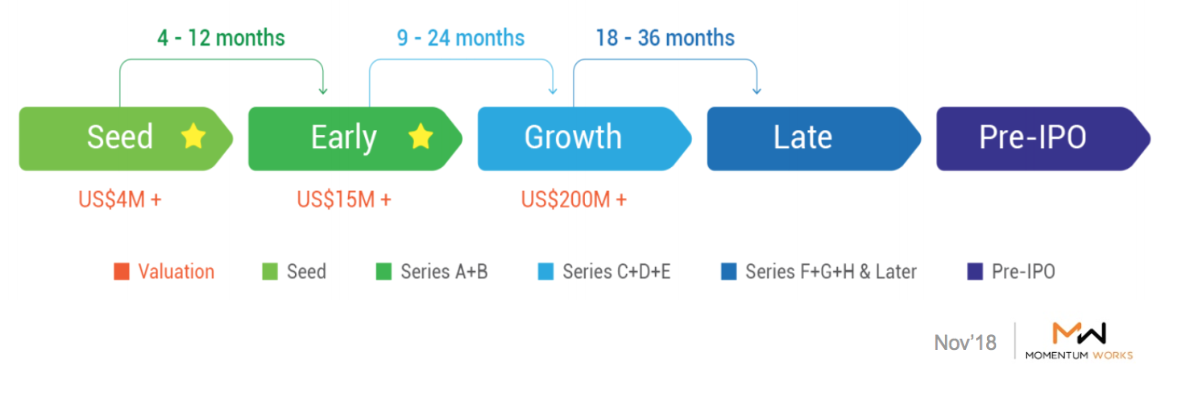
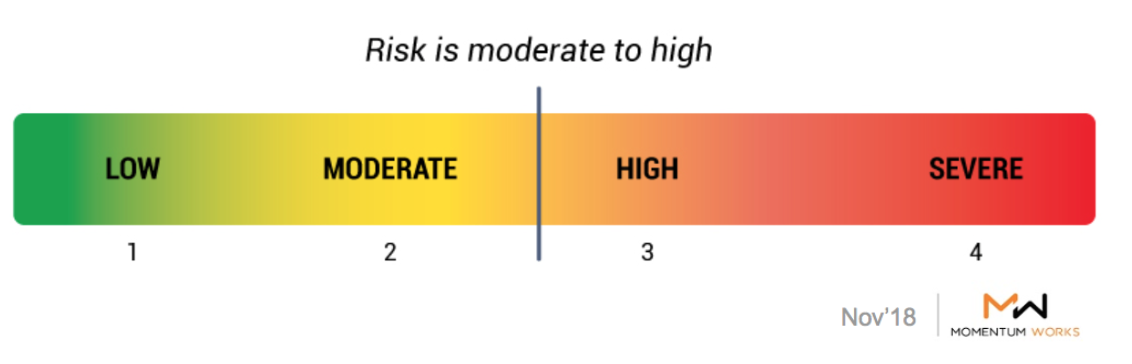
Highlights
- Indonesia’s fintech industry is very competitive but potential is still highly unrealised
- P2P lending and payments are the leading verticals comprising 69% of the Fintech landscape
- High unbanked population (51%) and large number of underserved SMEs are credit constrained; finance gap of $77.2 billion serves as a potential for fintech to step in
- Investments and consolidations expected to happen in the highly fragmented market
- Investors and startups need to account for moderate to high risks due volatile and increasingly strict regulatory environment as well as weakened Rupiah
You can buy the full report to find more detailed analyses and unique insights.

- What are the reasons for lack of financial inclusion that present opportunities for fintech players?
- What can fintech players do to fill in the $73B annual gap in financing needs?
- How can payment apps act as proxies to ATMs and bank accounts in this cash dependent market?

- How has fintech in Indonesia evolved from 2009 till now and what major events have disrupted the market?
- Which players had their licenses suspended/revoked and why?
- Which fintech companies have been raising funds and how have the round sizes evolved? Who are the active investors in this sector?

- What regulations are being tightened and what are the risks associated with it for fintech players?
- How is the poor currency performance going to affect overseas lenders and investors?
- How are consumer reactions imposing regulatory changes in debt collection methods? How will this affect the profitability of P2P lenders?










![[New Report] Food delivery platforms in Southeast Asia (SEA) 4.0](https://i0.wp.com/thelowdown.momentum.asia/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Food-delivery-platforms-in-Southeast-Asia-2024-_MW_Jan-2024-2.jpg?resize=100%2C70&ssl=1)
![[New report] Southeast Asia spends US$3.4 billion on modern coffee in 2023](https://i0.wp.com/thelowdown.momentum.asia/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Coffee-in-Southeast-Asia_MW_Nov-2023-1.png?resize=100%2C70&ssl=1)
![[New report] Apples to Apples 3.0: Benchmarking major tech platforms – what’s next after achieving profitability?](https://i0.wp.com/thelowdown.momentum.asia/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Apples-to-Apples-3.0_benchmarking-major-tech-platforms_whats-next-after-profitability_MW_Sept-2023-7.jpg?resize=100%2C70&ssl=1)

![[Press release] Frontline turnover costs businesses US$22.6 billion annually in Southeast Asia: Momentum Works and Lark report](https://i0.wp.com/thelowdown.momentum.asia/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Transforming-frontline-industries_MWLark_July-2024-6.jpg?resize=100%2C70&ssl=1)
![[New report] Transforming frontline industries](https://i0.wp.com/thelowdown.momentum.asia/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Transforming-frontline-industries_MWLark_July-2024.jpg?resize=100%2C70&ssl=1)



